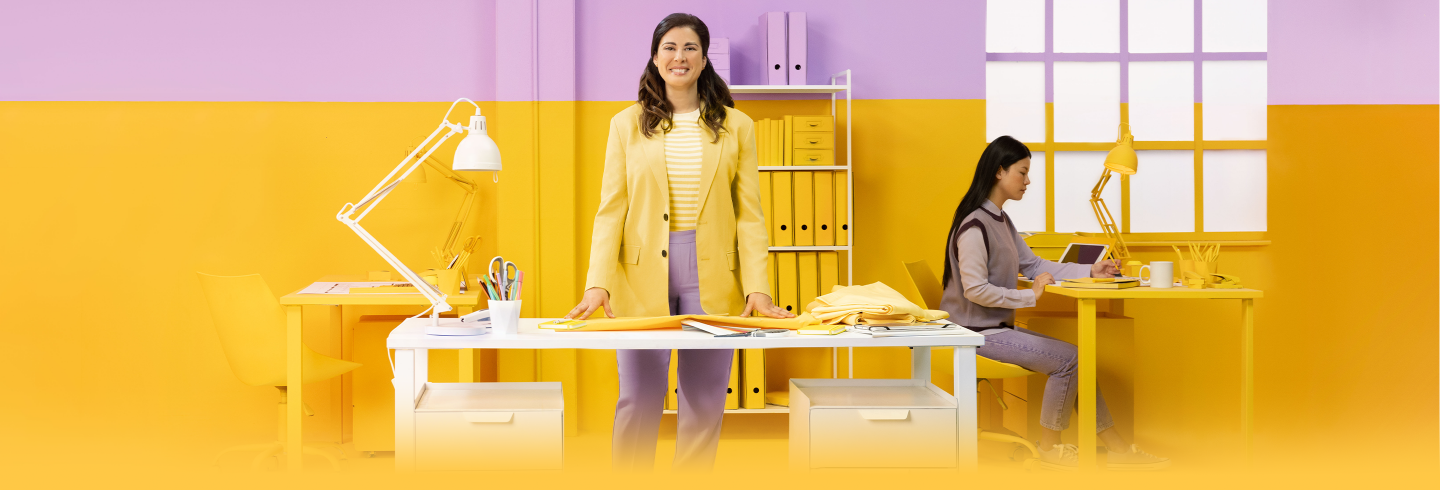

Excessive daytime sleepiness (EDS) due to obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) can disrupt many parts of your life
Excessive daytime sleepiness (E D S) due to obstructive sleep apnea (O S A) can disrupt many parts of your life 9/10 people with E D S due to O S A reported problems with their work, social life, and relationships due to their symptoms. *Footnote: Findings based on a study of focus groups conducted with 42 individuals experiencing EDS due to O S A People with E D S due to O S A are ~37% more likely to have depression and ~50% more likely to have anxiety compared to people with O S A without E D S.† Footnote: Findings based on a real-world study of 476 individuals, including individuals with E D S and those without E D S.
People with E D S due to O S A are ~37% more likely to have depression and ~50% more likely to have anxiety compared to people with O S A without E D S.† Footnote: Findings based on a real-world study of 476 individuals, including individuals with E D S and those without E D S.
SUNOSI is not indicated to treat depression or anxiety.
CPAP alone might not be enough to
improve wakefulness
Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) is a machine that is commonly used to help treat O.S.A.
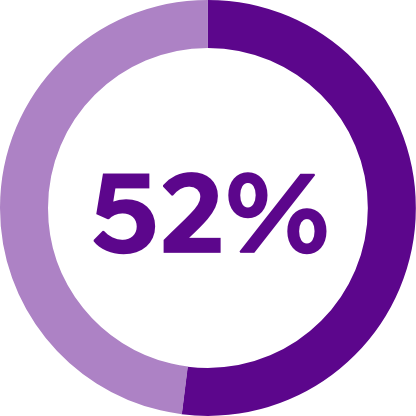 of people with O S A who use CPAP reported feeling sleepy during the day‡ Footnote: Findings based on a clinical trial of 174 patients with moderate to severe O S A
of people with O S A who use CPAP reported feeling sleepy during the day‡ Footnote: Findings based on a clinical trial of 174 patients with moderate to severe O S A
This is because OSA can disrupt chemicals in the brain, called neurotransmitters, that keep you
awake during the day. This may cause EDS in some people. Treating the disruptions can help manage EDS.
Disruption to your airways
When your airways repeatedly get blocked while you sleep, it can cause shallow breathing or cause your breathing to repeatedly stop. CPAP helps treat this disruption.
Disruption to your brain
Repeated sleep interruptions can harm parts of the brain that control feeling awake or sleepy. This can disrupt the activity of chemicals (neurotransmitters) in the brain, which can make you feel sleepy during the day. Wake-promoting agents, like SUNOSI, are thought to treat these disruptions.
SUNOSI is thought to improve wakefulness by increasing the activity of 2 wakefulness neurotransmitters: dopamine and norepinephrine.§
Download our quick reference guide to EDS due to O.S.A..
If EDS is making it hard to get through
your
day, you’re not alone
When I started to feel sleepy more often, I struggled to pay attention. As my law career progressed, I gained more responsibility, but as my sleepiness grew, my performance at work began to suffer.”
Here’s how EDS due to OSA is diagnosed
To diagnose EDS, your discussion with your healthcare provider may include answering a quiz called the Epworth Sleepiness Scale (ESS). In this quiz, you’ll answer questions about your likelihood of falling asleep in everyday situations
Many types of healthcare providers can help diagnose EDS due to O.S.A., including:- primary care doctor
- sleep specialist
- pulmonologist
- neurologist
- psychiatrist
- nurse practitioner
- physician assistant
Five simple questions can help you start a conversation with your healthcare provider.
Start questionnaireDo not take SUNOSI if you are taking, or have stopped taking within the past 14 days, a medicine used to treat depression called a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI).
Before taking SUNOSI, tell your doctor about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
- have heart problems, high blood pressure, kidney problems, diabetes, or high cholesterol.
- have had a heart attack or a stroke.
- have a history of mental health problems (including psychosis and bipolar disorders), or of drug or alcohol abuse or addiction.
- are pregnant or planning to become pregnant. It is not known if SUNOSI will harm your unborn baby.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if SUNOSI passes into your breast milk. Talk to your doctor about the best way to feed your baby if you take SUNOSI.
- SUNOSI does not treat the underlying cause of O.S.A. and SUNOSI does not take the place of any device prescribed for O.S.A., such as a continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) machine. It is important that you continue to use these treatments as prescribed by your healthcare provider.
Do not take SUNOSI if you are taking, or have stopped taking within the past 14 days, a medicine used to treat depression called a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI).
Before taking SUNOSI, tell your doctor about all of your medical conditions, including if you:- have heart problems, high blood pressure, kidney problems, diabetes, or high cholesterol.
- have had a heart attack or a stroke.
- have a history of mental health problems (including psychosis and bipolar disorders), or of drug or alcohol abuse or addiction.
- are pregnant or planning to become pregnant. It is not known if SUNOSI will harm your unborn baby.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. SUNOSI passes into your breast milk. Talk to your doctor about the best way to feed your baby if you take SUNOSI.
The most common side effects of SUNOSI include:
- •headache
- •nausea
- •decreased appetite
- •anxiety
- •problems sleeping
SUN CON ISI 06/2023
Please see Medication Guide.
- SUNOSI does not treat the underlying cause of O.S.A. and SUNOSI does not take the place of any device prescribed for O.S.A., such as a continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) machine. It is important that you continue to use these treatments as prescribed by your healthcare provider.
Do not take SUNOSI if you are taking, or have stopped taking within the past 14 days, a medicine used to treat depression called a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI).
Before taking SUNOSI, tell your doctor about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
- have heart problems, high blood pressure, kidney problems, diabetes, or high cholesterol.
- have had a heart attack or a stroke.
- have a history of mental health problems (including psychosis and bipolar disorders), or of drug or alcohol abuse or addiction.
- are pregnant or planning to become pregnant. It is not known if SUNOSI will harm your unborn baby.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if SUNOSI passes into your breast milk. Talk to your doctor about the best way to feed your baby if you take SUNOSI.